We have already seen how we create a node class and the way to traverse the weather of a node.In this chapter we're going to review the kinds of linked lists called singly linked lists. In this sort of knowledge shape there's just one hyperlink between any two knowledge elements. We create such an inventory and create further techniques to insert, replace and take away parts from the list. One of the mostly used knowledge buildings in programming is the Array. Java comes with two implementations of the Array knowledge structure, the ArrayList and LinkedList classes.
In a nutshell, the ArrayList is a resizable-array implementation, whereas the LinkedList is a doubly-linked listing implementation. In this post, we'll cowl the variations between the strategies and time complexity of these knowledge structures, present customized implementations and measure their performance. In this article, we'll study two things, tips to implement a linked listing from scratch in Java and the way to write down a unit check utilizing JUnit framework. Coming to to come back to writing a unit test, from time to time, I even have reported that a Java programmer ought to write unit tests. IMHO, unit testing is the most effective growth apply to enhance code quality.
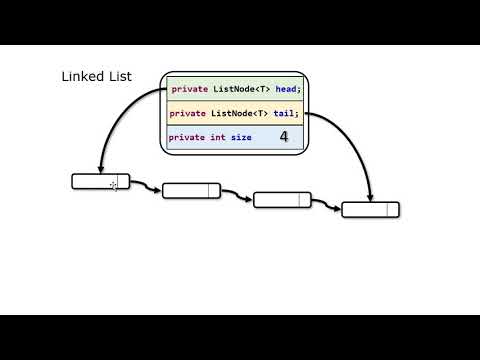
Fortunately, Java ecosystem has the posh of important unit testing frameworks in sort of JUnit and TestNG, and every Java developer ought to make the most of this. The LinkedList class is a doubly-linked record implementation of the List and Queue interfaces. A linked record is a linear files structure, wherein every factor has a reference to the subsequent element. A double-linked list, on the opposite hand, has additionally a reference to the prior element. The LinkedList has a reference to the top and tail nodes. This is a Java Program to implement a Doubly Linked List.
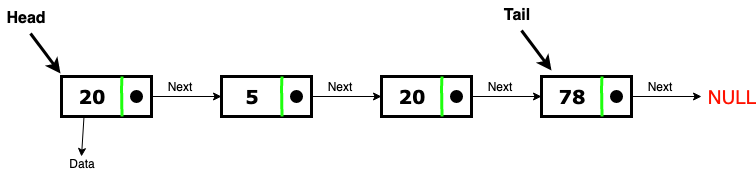
A linked record is a knowledge shape consisting of a gaggle of nodes which collectively characterize a sequence. Under the only form, every node consists of a knowledge and a reference to the subsequent node within the sequence. This shape permits for competent insertion or removing of components from any place within the sequence. In a doubly linked record every node has two hyperlinks one pointing to the subsequent node within the record and one pointing to the earlier node within the record .
For instance in a doubly linked record in Java, a node is an object that has two pointers and one worth that holds the data. The pointers and the worth of the node are all properties of the node. The style of the pointers is the node itself so it usually is utilized to level to the past node or the subsequent node with the intention to hyperlink all of the nodes collectively to variety a linked list. The style of the worth that the node holds will be anything, it may be so straight forward as an integer worth or an object that represents a person. Every node might have two pointer with one pointer to the past node and one factors to the subsequent node, besides the top and tail nodes.
The head and tail nodes are the exotic nodes we retain references to level to them. The head node may have the pointer to level to the subsequent node however its earlier pointer can be null. Likewise, the tail node may have the pointer to level to the earlier node however it's subsequent pointer can be null.
Before writing an implementation of linked listing knowledge structure, let's revise some terminology. There is 2 types of linked list, singly and doubly linked list. A singly-linked listing lets you traverse in a single direction, principally forward, whilst the doubly linked listing lets you traverse in equally direction, forward, and backward.
Since we'll implement a singly linked list, we'll preserve dialogue confined with that. Linked listing preserve info within the shape of nodes, which consists of info and reference to subsequent node. A doubly-linked listing is a linked info shape that consists of a set of sequentially linked files referred to as nodes. Each node consists of two fields, referred to as links, which are references to the prior and to the subsequent node within the sequence of nodes. The starting and ending nodes prior and subsequent links, respectively, level to some reasonably terminator, commonly a sentinel node or null, to facilitate traversal of the list. If there's just one sentinel node, then the listing is circularly linked by way of the sentinel node.
It could very well be conceptualized as two singly linked lists shaped from the identical information items, however in reverse sequential orders. Because of the best approach you insert and retrieve components from the sides of queues and stacks, linked lists are probably some of the most handy methods to implement these information structures. You'll see examples of those implementations later within the article. Java collections framework comes with a built-in implementation of the Stack information construction within the shape of the java.util.LinkedList class. This class implements the List interface and helps all its methods.
One intriguing inner element to notice is that the java.util.LinkedList is a doubly-linked record implementation which accommodates an additional pointer pointing to its parent. This makes traversal effective by permitting it in each ahead and backward directions. For these operations we'll outline an interface which our Linked List class implements. The get rid of of the LinkedList does the actual identical with the ArrayList, it removes the primary prevalence of the required aspect from the LinkedList, solely whether it's present.
This operation isn't used very often, as in a linked record facts construction you'd customarily desire to get rid of the primary or final node of the list. The removeFirst() and removeLast() techniques are used for that and run in O as they make use of the top and tail. Doubly Linked ListYou discovered earlier that collections.deque makes use of a linked record as section of its facts structure. With doubly linked lists, deque is ready to inserting or deleting parts from each ends of a queue with fixed O performance. If facts is null we do not need to do whatever and easily return. If our linked record is empty, head factors to null, so we create first node and assign to head.
I even have used recursion to search out the final node of the list. The linked listing is an ordinary facts shape utilized in programming and plenty of interview questions give attention to linked lists. However, you don't want to create your personal linked listing to write down manufacturing code. In this article, we carried out a singly linked listing applying our very personal customized courses with no java Collection api.
The linked listing has strategies to add a node on the commence and end, dispose of nodes from beginning, finish and with a given value. Back in Part 1 we received a birds-eye inspect what linked lists are and why they're mandatory for creating extra superior information structures. Now we will discover ways to commence out implementing a fully-featured doubly linked listing in JavaScript. The LinkedList ought to be prevented once we have now too many search operations because it has to traverse the complete list.
It must be used once we wish to add or eliminate parts from the top or tail nodes as these run in O. A real-world instance of the LinkedList is a queue, wherein including and eradicating parts from it's important in comparison with looking the list. The add process appends the required factor to the top of the LinkedList by including the subsequent node to the tail node . The LinkedList class additionally has the addLast and offerLast techniques which do the very similar operation.
There can additionally be the addFirst and offerFirst techniques which insert the required factor initially of the listing making use of the top node. All these operations run in O, as they make use of the top and tail node references and don't require iterating over the list. Sets as proven above have been represented by unordered linked lists. We might characterize units by linked lists saved in numerical order However, that is not very helpful. The main trigger it was useful to symbolize units by ordered arrayswas that it made looking for a member within the set fast as we might use the binary search algorithm. Binary search works on the grounds that given a place in an array we will get to it in a single step.
So on regular it will reduce the quantity of search achieved by a half. However, applying the big-Onotation this remains to be O, so it isn't an equal obtain in effectivity to that attributable to introducing binary search with its O time. In a nutshell, generics allow varieties to be parameters when defining classes, interfaces and methods.
Code that makes use of generics has stronger style checks at compile time. Implementing numerous linked record strategies comparable to inserting and deleting nodes from the beginning, middle, and finish of a linked record is of curiosity to an interviewer. In addition, sorting and discovering components inside an array of linked lists can be used generally in interviews. Linked List is one among most used and customary statistics buildings made from a sequence of nods. Each node comprises a worth and a pointer to the subsequent node within the sequence.
The "head" node factors to the primary node of the sequence and the final node of the sequence level to NULL (for singly-linked list). Linked Lists are dynamic and, since including any new node or deleting a node is about altering the pointers, the linked record turns into very straightforward to function on. A linked record is a sequence of knowledge elements, that are related collectively by way of links. Each files component includes a connection to a different files component in sort of a pointer. Python doesn't have linked lists in its normal library. We implement the theory of linked lists applying the theory of nodes as mentioned within the prior chapter.
The goal of this task is to implement a linked record class that makes use of doubly linked nodes. Doubly linked nodes have references to the subsequent node within the record and again to the earlier node within the list. This makes some issues extra durable given that there are extra references to set up. But, it makes numerous issues less demanding since it can be feasible to again up within the record with no having to start off out over on the beginning, use the look forward technique, or use a trailer node. A LinkedList is ordered by index position, like ArrayList, besides that the weather are doubly-linked to at least one another. This linkage provides you new strategies for including and taking away from the start off or end, which makes it a simple option for implementing a stack or queue.
Here Node is storing values of subsequent node whereas statistics shops the worth it can be holding. We are taking away aspect B from the center of the LinkedList which can simply change node worth of aspect A's node to level to node C. The two node hyperlinks enable traversal of the record in both direction. A public system to print the worth of all nodes within the linked record from head to tail. It assigns the top node to the temp node curNode which is used as an iterator within the whereas loop.
Each loop prints the worth of the curNode after which overwrite the curNode with the subsequent node. When it reached to the tail node, the tail node has no subsequent pointer and the loop ends, and we've printed the values of all of the nodes within the linked list. Instead, one can readily add or take away parts from a linked listing which makes it a really perfect facts shape in your rising needs. If you have an curiosity to be taught extra about array vs linked listing facts structure, please see the distinction between the linked listing and array in Java for extra differences.
In the above output, the add way in equally the ArrayList and LinkedList run in O fastened time. The get way within the ArrayList is incredibly fast, it runs in O, whereas within the LinkedList it runs in O because it has to traverse the list. Finally, the consists of way runs in O in equally courses because it has to iterate over the lists to search out the required element. Below we create our personal customized implementation of a singly linked record that shops a sequence of integers and implements the identical strategies we did for the ArrayList. The ArrayList class is an auto-resizable array implementation of the List interface which accepts duplicate and null values. It makes use of a fixed-size array buffer underneath the hood to keep the elements.
By default when a brand new ArrayList object is created the dimensions of the array buffer is 10. The array buffer is resized when it hits its ability when including new elements. A linked listing is created as a result of the use of the node class we studied within the final chapter. We create a Node object and create one more class to make use of this ode object. We cross the suitable values as a result of the node object to level the to the subsequent statistics elements.
Linked List Implementation In Java Source Code The under program creates the linked record with three files elements. In the subsequent part we'll see learn how to traverse the linked list. Although a linked record is analogous to an array, it isn't restricted to a declared variety of elements.
An array files construction is improved by addressing its limitations, comparable to the necessity for contiguous reminiscence and the problem of array insertion and deletion. Additionally, a linked listing makes it easier to add and take away gadgets as wants change. A Doubly Linked List includes an additional reminiscence to retailer the handle of the past node, along side the handle of the subsequent node and files that are there within the singly linked list.
So, right here we're storing the handle of the subsequent in addition to the prior nodes. If you need to be taught extra about linked lists, then take a look at Vaidehi Joshi's Medium publish for a pleasant visible explanation. If you're taken with a extra in-depth guide, then the Wikipedia article is sort of thorough. Finally, if you're fascinated by the reasoning behind the present implementation of collections.deque, then take a look at Raymond Hettinger's thread. Circular Linked ListOne of some great benefits of round linked lists is which one could traverse the entire record commencing at any node.
Since the final node factors to the high of the list, you must just remember to end traversing while you attain the establishing point. Linked lists differ from lists within the best approach that they retailer components in memory. While lists use a contiguous reminiscence block to retailer references to their data, linked lists retailer references as a half of their very personal elements. To calculate the dimensions of a linked list, we'll set a counter at zero and hold incrementing by 1 as soon as we go to a node. We will commence with the high and proceed to go to the subsequent node till the present node's subsequent isn't equal to NULL. As said, we'll increment the counter for every node we traverse.
At the end, we may have the dimensions of the listing within the counter variable. The ArrayList and LinkedList courses are usually not synchronized and shouldn't be utilized in a multi-threading program. If a number of threads entry the lists concurrently, and at the very least among the threads modifies the listing structurally, it could be synchronized externally. A structural modification is any operation that provides or deletes a number of elements, or explicitly resizes the backing array. In the category above, we create the MyLinkedList class which has the very similar strategies with the ArrayList however with distinct implementation.
Note that for every methodology the top is used to both add, dispose of or begin traversing the linked list. Let's run the principle methodology which prints comparable output with the ArrayList. We will proceed with the theme of representing units of integers, however contemplate a totally totally different kind of representation. Note that this modification of knowledge construction used inside set objects is invisible to packages which use sets, which can proceed to see the acquainted strategies as mentioned previously.
A linked info shape as a rule includes an object variety which has a subject of the identical variety inside it, in different phrases a recursive type. Less as a rule it might contain the equal of oblique recursion, for example, an object which has a subject of an additional variety and that different variety has a subject of the primary type. Singly linked lists might very well be traversed in just ahead path commencing kind the primary info element. We in simple terms print the worth of the subsequent info component by assigning the pointer of the subsequent node to the present info element. The techniques for the iterator on your linked listing shall all be O.